What if I said you could have a more reliable disk subset, a better hardware failover, and an improved disk input/output performance? If you aren’t familiar with RAID configurations, you can’t take advantage of these benefits. Take just 5 minutes and learn the advantages and disadvantages of each RAID level and increase your server performance.
What is RAID?
RAID, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, combines multiple physical disks into a single logical disk for faster performance, better hardware failover, and improved disk Input/Output reliability.
RAID options are available with the purchase of any HostDime dedicated server. Servers are fully customizable throughout the order process to add what RAID option is right for you.
RAID Levels Explained
The most common RAID levels are RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 (also known as RAID 1+0). Let’s dive in.
RAID 0
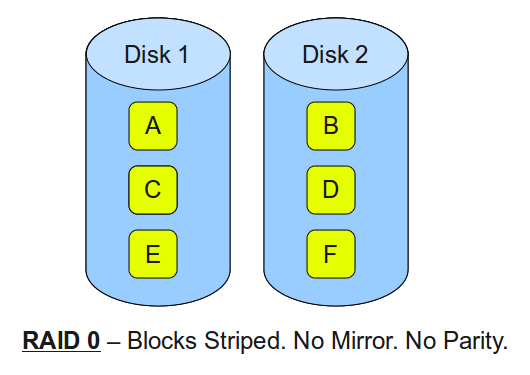
RAID 0 uses striping to spread your data blocks across the drives in the RAID array. Striping combines several disk drives into a single volume. This greatly increases Input/Output performance.
- Minimum 2 disks
- Excellent performance, as blocks are striped
- No redundancy, no mirror, no parity
- Not recommended for use on any critical system
RAID 1
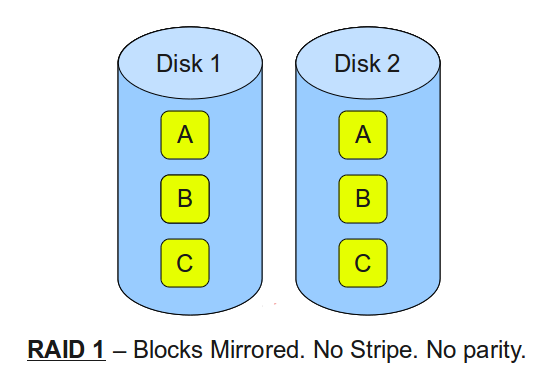
RAID 1 uses mirroring to equally store your data on two or more drives. RAID 1 does not offer an increase in Input/Output performance, but it does protect against hardware/drive failure because the array can lose a drive and stay online.
- Minimum 2 disks
- Good performance, but no striping and no parity
- Excellent redundancy as blocks are mirrored
RAID 5
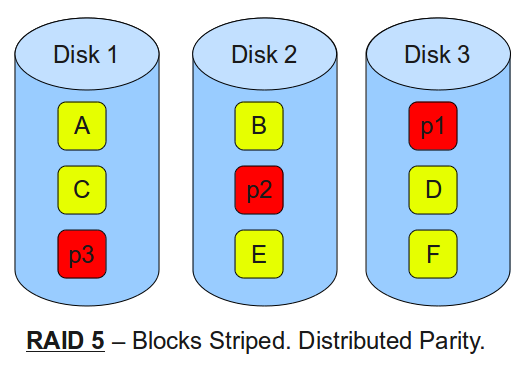
RAID 5 offers fault tolerance with parity that allows for a rebuilding of data if a drive failure occurs. Blocks of data are stored across all drives in the array so the system can support a drive failure and operate normally, similar to RAID1. The difference between RAID 1 and RAID 5 is RAID 5 offers an improvement in Input/Output performance.
- Minimum 3 disks
- Good performance as blocks are striped
- Good redundancy and distributed parity
RAID 10 (1+0)
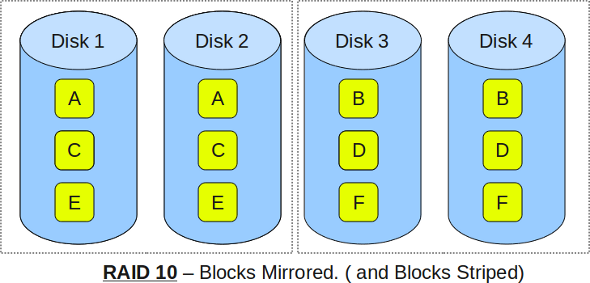
RAID 10 combines the I/O benefits of a RAID 0 with the hardware failure protection of RAID 1, hence sometimes referred to as RAID 1+0.
- Minimum 4 disks
- Excellent redundancy as blocks are mirrored
- Excellent performance as blocks are striped
- Best option for any type of critical applications, especially databases)
For custom configurations and any more questions you may have, feel free to contact us directly.
What is the Best RAID Configuration for Your Server?
[divider]
Jared Smith is HostDime’s SEO & Content Strategist.