
If you’re reading this, you’re probably familiar with RAID, the method that combines multiple disks for increased performance and hardware failover. RAID options are available with the purchase of any HostDime dedicated server. Use our RAID calculator to compare RAID drive sizes to increase your server’s performance!
While RAID solutions excel at data storage and protection, you have to sacrifice a little bit of speed. To combat this and keep things running fast, there’s configuration options like BBU, CacheVault, and CacheCade. Let’s dive into the benefits of each.
Battery Backup Unit (BBU)
Let’s present a nightmare scenario. Your dedicated server loses power before changes have left the cache and committed to disk, resulting in corrupted data. The contents on the RAID card become unrecoverable and you may not know what files are damaged.
To help protect against this data loss, we offer customers a BBU at $20 a month. A BBU is a physical lithium ion batter that you connect to the RAID controller.

The BBU’s job is to remember the data that hasn’t been synced to disk yet, usually up to 72 hours without power. When the machine powers back up, the BBU will write the cache contents on the disk.
If your “write cache” option is set to “write through” or “off”, then you should be fine without a BBU on your raid card. The downside to having “write cache” turned off is the RAID performance will be sub-optimal. Many RAID cards will have the write cache setting “on” only if the BBU is installed. This is very important for users who frequently save their database from certain types of corruption or need high data integrity.
CacheVault Cache Protection
Similar to BBUs, CacheVault is a physical module that connects to RAID controllers. It does exactly what the BBU does, but is a newer technology that enables other features.

On the RAID controller, when write-back mode is enabled, data is temporarily stored in DRAM until the RAID controller writes that information to the disk. As discussed above, if power fails without a BBU the data is lost but if power fails with a BBU it’s stored in DRAM for up to 72 hours.
What makes CacheVault superior in this aspect is the ability for that data to be moved from DRAM to NAND flash. When the data is moved from DRAM to NAND flash, it can be stored there for up to 3 years! When the server turns back on, data is moved from NAND back to DRAM and then written to the disks. Operations then continue as if nothing ever happened. Here’s a video that goes into more detail:
HostDime offers customers with RAID cache protection CacheVault for $30 a month.
CacheCade SSD Cache
While BBU and CacheVault are both physical module add-ons, CacheCade is a RAID controller software that enables an SSD Read/Write cache for the array. It allows you to optimize the existing HDD arrays with the SSD-based flash cache.
With the latest tech advancements pushing HDD arrays to reach their input/output potential, data “hot spots” are inevitable. Hot spots are the areas most commonly accessed on HDD arrays; when you have hot spots, the life of the drives are severely shorten.
To fix this problem, CacheCade will create a front-side flash cache for the “hottest” array. This flash cache reads/writes to the SSD which is much more efficient than reading/writing to the HDD array. CacheCade content remains intact upon reboot. Here’s a diagram showing how it works:
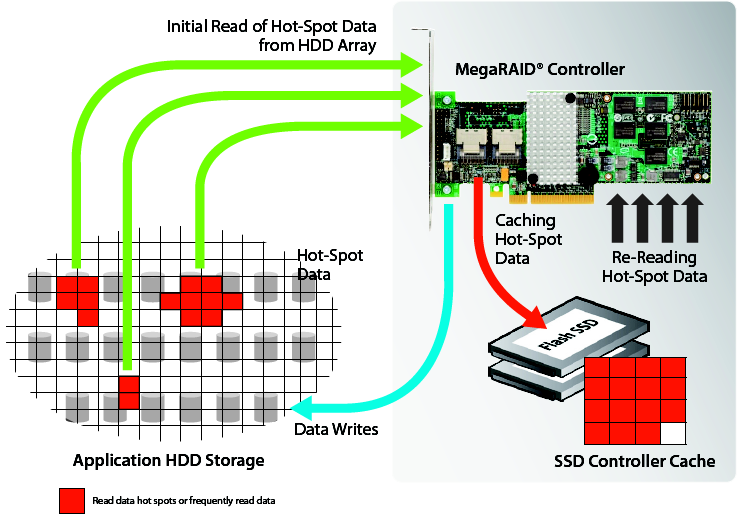
HostDime offers CacheCade installation for a small fee. Open a chat with us and we’ll get it started for you.
[divider]
This article was written by HostDime’s SEO & Content Strategist Jared Smith and HostDime’s Senior Data Center Sales and Product Manager Marcos Font.
